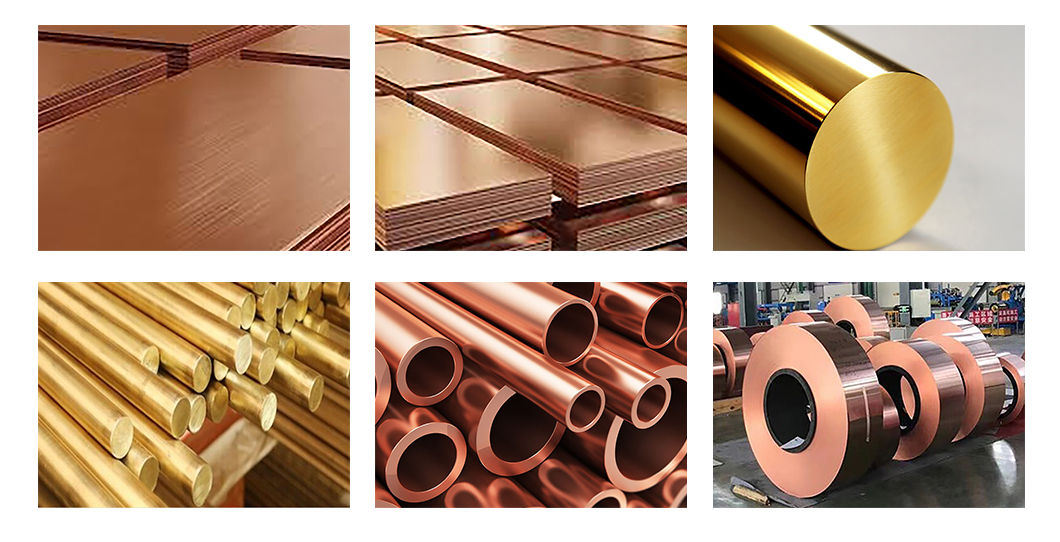
Products
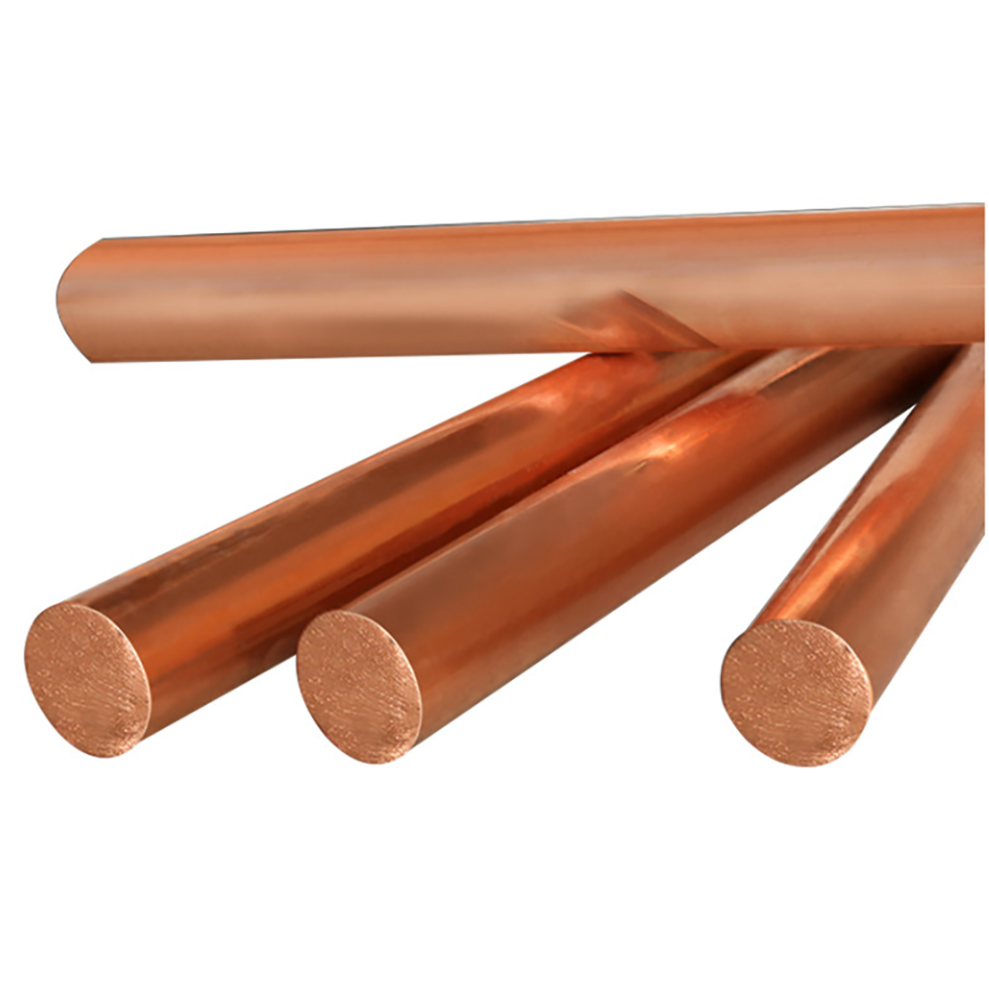
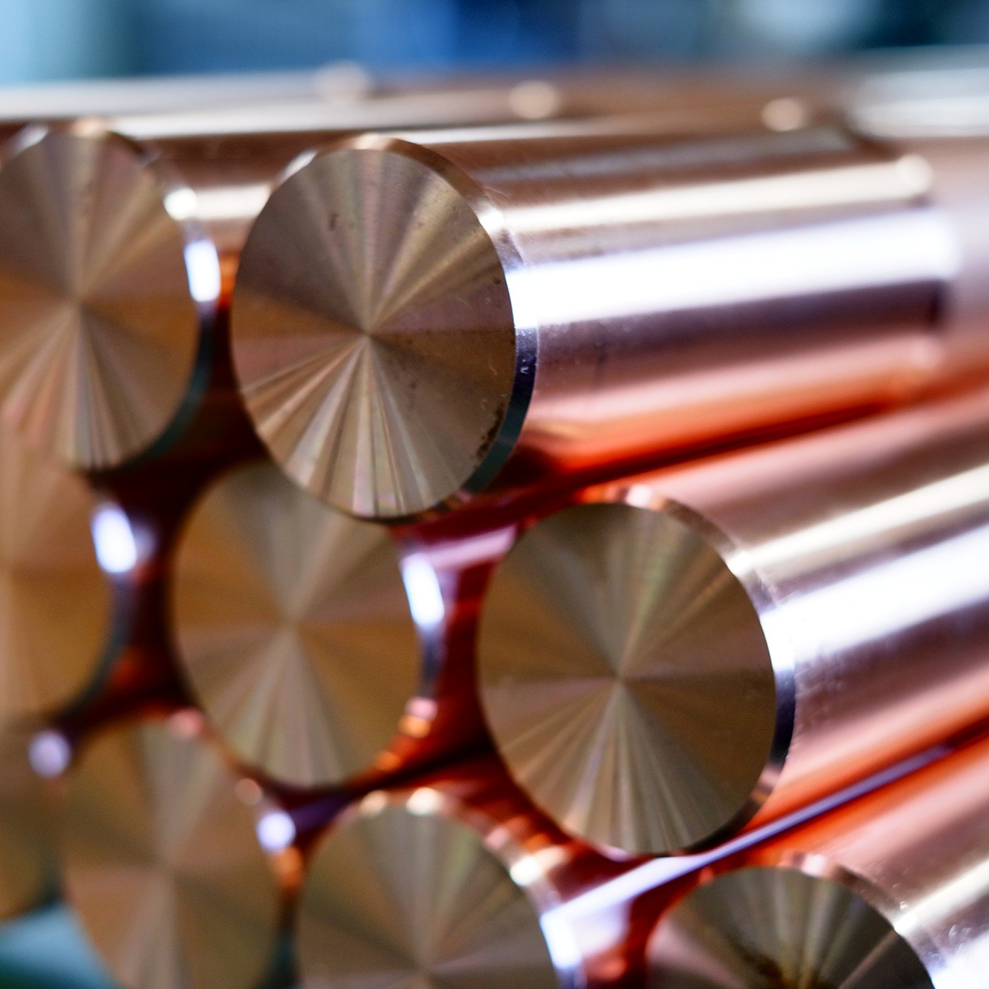






Shape Round Bar
Surface Treatment Polished
Material Type Pure Copper, Brass, White Copper, Bronze
Application Automotive Components, Industrial Machinery…
Common Grades T1, T2, T3, Tu1, Tu2, H65, H68, Hpb59-1, B19, B25
Categories: Copper Alloy Series
|
Pure copper
|
|
|
Common grades
|
T1, T2, T3, TU1, TU2
|
|
Characteristics
|
Conductive
|
|
Common uses
|
Electrical switches, motor coils, electronic components, air conditioning piping, soft welding gun heads
|
|
Brass
|
|
|
Common grades
|
H59, H62, H65, H68, HPb59-1 (easy-to-machine brass)
|
|
Characteristics
|
High strength, wear-resistant, resistant to water vapor corrosion
|
|
Common uses
|
Architectural hardware, heat exchanger tubes, pumps, power cylinders and bushings, military supplies
|
|
White copper
|
|
|
Common grades
|
B19, B25, BFe10-1-1, BZn15-20, BA13-3
|
|
Characteristics
|
Stable physical properties at room temperature
|
|
Common uses
|
Medical equipment, precision instruments, thermocouples, clock parts, eyeglass frames
|
|
Bronze
|
|
|
Common grades
|
QCr 0.5, QCr 0.6-0.4-0.05, QSn 4-3, QSn 6.5-0.4, QSn 7-0.2, QAl 5, QAl 9-2, QAl 10-4-4, QSi 3-1, QSi 3.5-3-1.5, QMn 1.5, QMn 5, QCd 1
|
|
Characteristics
|
Different formulations based on hardness, strength, elasticity, high-temperature conductivity, etc.
|
|
Common uses
|
Lamp spring clips, switch spring clips, resistance welding electrode materials (rolling welders, butt welders, contact welders, riveting welders), chromium-zirconium copper, beryllium-cobalt copper
|
|
CuNi2 NC005
|
1
|
2
|
4
|
6
|
8
|
3
|
10
|
14
|
|
|
CN3W
|
CN5W
|
CN7W
|
CN10W
|
CN12W
|
QMn3
|
CN15W
|
CN20W
|
||
|
TYPE
|
CuNi1
|
CuNi2CuNi4
|
CuNi6
|
CuNi8
|
CuMn3
|
CuNi10
|
CuNi14
|
||
|
NC003
|
NC005NC007
|
NC010
|
NC012
|
MC012
|
NC015
|
NC020
|
|||
|
Composition(%)
|
Cu
|
Rest
|
Rest
|
Rest
|
Rest
|
Rest
|
Rest
|
Rest
|
Rest
|
|
Mn
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
3
|
—
|
0.3
|
|
|
Ni
|
1
|
2
|
4
|
6
|
8
|
10
|
14.2
|
||
|
Max.continuous operating temperatureC
|
200
|
200
|
200
|
220
|
250
|
200
|
250
|
300
|
|
|
μΩ ·m(20℃)Resistivity
|
0.03±10%
|
0.05±10%
|
0.07±10%
|
0.10±10%
|
0.12±10%
|
0.12±10%
|
0.15±10%
|
0.20±5%
|
|
|
×105/℃
(20-600℃) Resistance-temperaturecoefficient |
<100
|
<120
|
<50
|
<60
|
<57
|
<38
|
<50
|
<38
|
|
|
Thermovoltage tocopperat20℃inμV/K
|
-8
|
-12
|
-12
|
-18
|
-22
|
–
|
-25
|
-28
|
|
|
Mean coefficient oflinearthermal expansion,in10/K,at a temperaturebetween20 ℃and400℃
|
17.5
|
17.5
|
17.5
|
17.5
|
17.5
|
18
|
17.5
|
17.5
|
|
|
Thermal conductance at20℃W/mK
|
145
|
130
|
130
|
92
|
75
|
84
|
59
|
48
|
|
|
Specific heat capacityat20℃J/gK
|
0.38
|
0.38
|
0.38
|
0.38
|
0.38
|
0.39
|
0.38
|
0.38
|
|
|
Densityat20℃(g/cm³)
|
8.9
|
8.9
|
8.9
|
8.9
|
8.9
|
8.9
|
8.9
|
8.9
|
|
|
Melting temperaturein℃
|
1085
|
1090
|
1090
|
1095
|
1097
|
1050
|
1100
|
1115
|
|
|
Min.tensile strengthin N/mm²
|
210
|
220
|
220
|
250
|
270
|
290
|
290
|
310
|
|
|
% Elongation
|
25
|
25
|
25
|
25
|
25
|
25
|
25
|
25
|
|
|
CuNi2 NC005
|
19
|
23
|
30
|
34
|
44
|
|
|
CN25W
|
CN30W
|
CN35W
|
CN40W
|
CN50W
|
||
|
TYPE
|
CuNi19
|
CuNi23
|
CuNi30
|
CuNi34
|
CuNi44
|
|
|
NC025
|
NC030
|
NC035
|
NC040
|
NC050
|
||
|
Composition(%)
|
Cu
|
Rest
|
Rest
|
Rest
|
Rest
|
Rest
|
|
Mn
|
0.5
|
0.5
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
|
|
Ni
|
19
|
23
|
30
|
34
|
44
|
|
|
Max.continuous operating temperatureC
|
300
|
300
|
350
|
350
|
400
|
|
|
μΩ ·m(20℃)Resistivity
|
0.25±5%
|
0.30±5%
|
0.35±5%
|
0.40±5%
|
0.49±5%
|
|
|
×105/℃
(20-600℃) Resistance-temperaturecoefficient |
<25
|
<16
|
<10
|
<-0
|
<-6
|
|
|
Thermovoltage tocopperat20℃inμV/K
|
-32
|
-34
|
-37
|
-39
|
-43
|
|
|
Mean coefficient oflinearthermal expansion,in10/K,at a temperaturebetween20 ℃and400℃
|
17.5
|
17.5
|
17
|
16
|
15
|
|
|
Thermal conductance at20℃W/mK
|
38
|
33
|
27
|
25
|
23
|
|
|
Specific heat capacityat20℃J/gK
|
0.38
|
0.38
|
0.39
|
0.4
|
0.41
|
|
|
Densityat20℃(g/cm³)
|
8.9
|
8.9
|
8.9
|
8.9
|
8.9
|
|
|
Melting temperaturein℃
|
1135
|
1150
|
1170
|
1180
|
1280
|
|
|
Min.tensile strengthin N/mm²
|
340
|
350
|
400
|
400
|
420
|
|
|
% Elongation
|
25
|
25
|
25
|
25
|
25
|
|
|
BMn3-12
|
|
|
Alloy Name
|
BMn3-12 (Manganese brass / Manganese bronze)
|
|
Common Grades (Nickel-based alloys reference)
|
Hastelloy C276, Hastelloy C22, Hastelloy C-2000, Hastelloy C-4, Hastelloy C, Hastelloy B, Hastelloy B-2, Hastelloy B-3, Hastelloy X, Hastelloy G-30, Hastelloy G-35
|
|
Chemical Composition (GB/T 5231-2022)
|
Cu ≈ 87%; Mn 11.5–13.5%; Fe 0.2–0.5%; C ≤ 0.05%; Si 0.1–0.3%; P ≤ 0.005%; S ≤ 0.02%; Ni 2–3.5% (Ni+Co total); Pb ≤ 0.02%; Al ≤ 0.2%; Mg ≤ 0.03%
|
|
Physical Properties
|
Density: ~8.4 g/cm³; Melting range: 961–1011.2 °C; Thermal expansion coefficient: 16×10-6 K-1(at 100 °C); Thermal conductivity: 21.8 W/(m·K); Specific heat capacity: 0.408 J/(kg·K); Electrical resistivity: 0.435×10-6 Ω·m; Temperature coefficient of resistivity: 0.00003 °C-1
|
|
Mechanical Properties
|
High hardness and wear resistance with good toughness and corrosion resistance; After quenching & aging: Tensile strength ≥ 400 MPa; Yield strength ≥ 300 MPa
|
|
Application Fields
|
Heavy industry, construction machinery, transportation vehicles, energy equipment, aerospace, automotive; Suitable for heavy-load parts such as bearings, bushings, gears, gearboxes, hydraulic system components
|
|
Processing & Manufacturing
|
Processing methods: casting, forging, extrusion, cutting; Heat treatment: quenching and aging to improve mechanical properties; Good weldability with various welding techniques
|

